Adversarial Structure Matching for Structured Prediction Tasks
Abstract
Pixel-wise losses, e.g., cross-entropy or L2, have been widely used in structured prediction tasks as a spatial extension of generic image classification or regression. However, its i.i.d. assumption neglects the structural regularity present in natural images. Various attempts have been made to incorporate structural reasoning mostly through structure priors in a cooperative way where co-occurring patterns are encouraged.
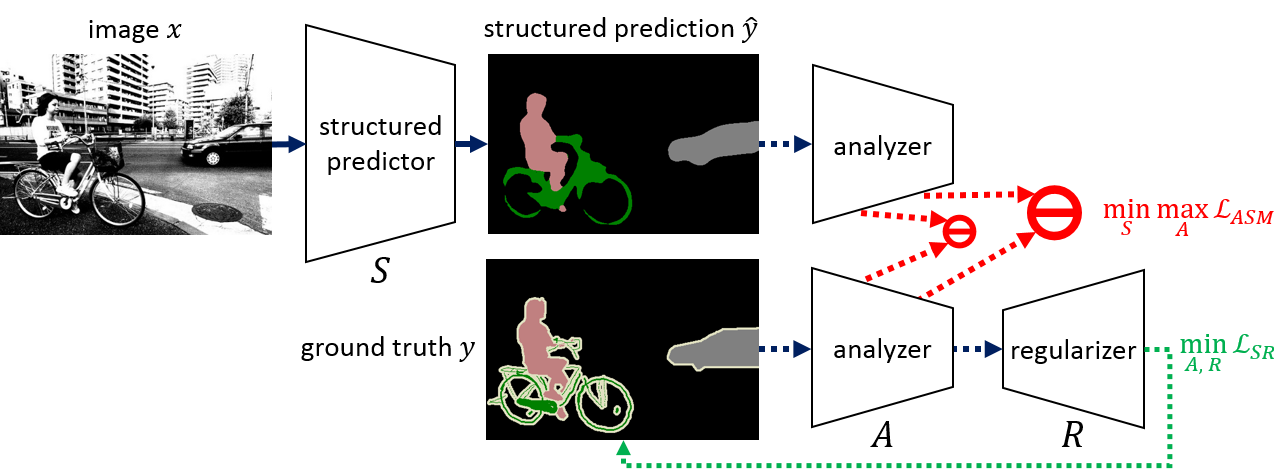
We, on the other hand, approach this problem from an opposing angle and propose a new framework, Adversarial Structure Matching (ASM), for training such structured prediction networks via an adversarial process, in which we train a structure analyzer that provides the supervisory signals, the ASM loss. The structure analyzer is trained to maximize the ASM loss, or to emphasize recurring multi-scale hard negative structural mistakes among co-occurring patterns. On the contrary, the structured prediction network is trained to reduce those mistakes and is thus enabled to distinguish fine-grained structures. As a result, training structured prediction networks using ASM reduces contextual confusion among objects and improves boundary localization. We demonstrate that our ASM outperforms pixel-wise IID loss or structural prior GAN loss on three different structured prediction tasks: semantic segmentation, monocular depth estimation, and surface normal prediction.
Citation
@inproceedings{asm2019,
title={Adversarial Structure Matching for Structured Prediction Tasks},
author={Hwang, Jyh-Jing and Ke, Tsung-Wei and Shi, Jianbo and Yu, Stella X},
booktitle={Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition},
pages={4056--4065},
year={2019}
}
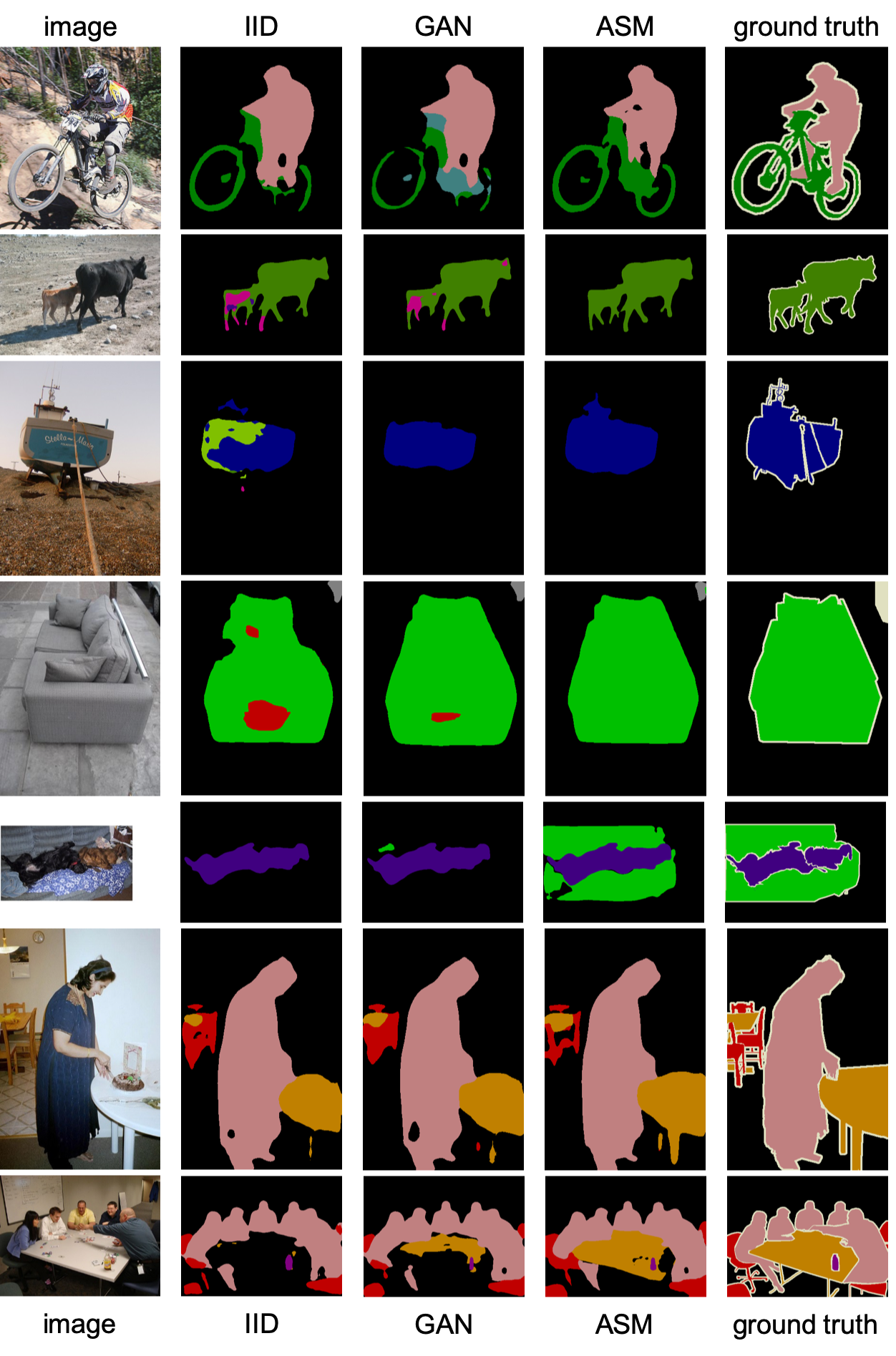
Semantic Segmentation on PASCAL VOC 2012

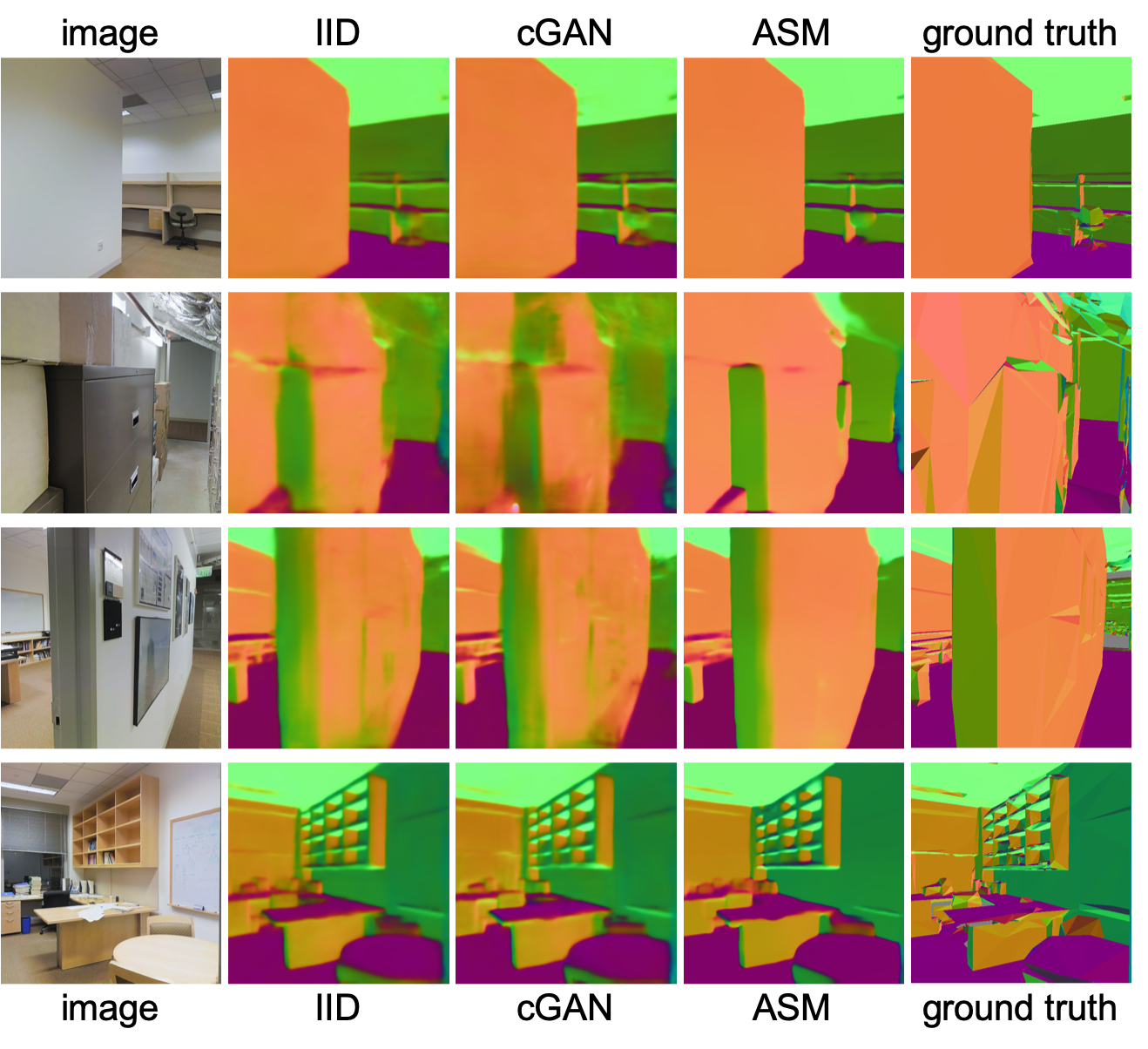
Surface Normal Prediction on Stanford-2D-3D-Semantic
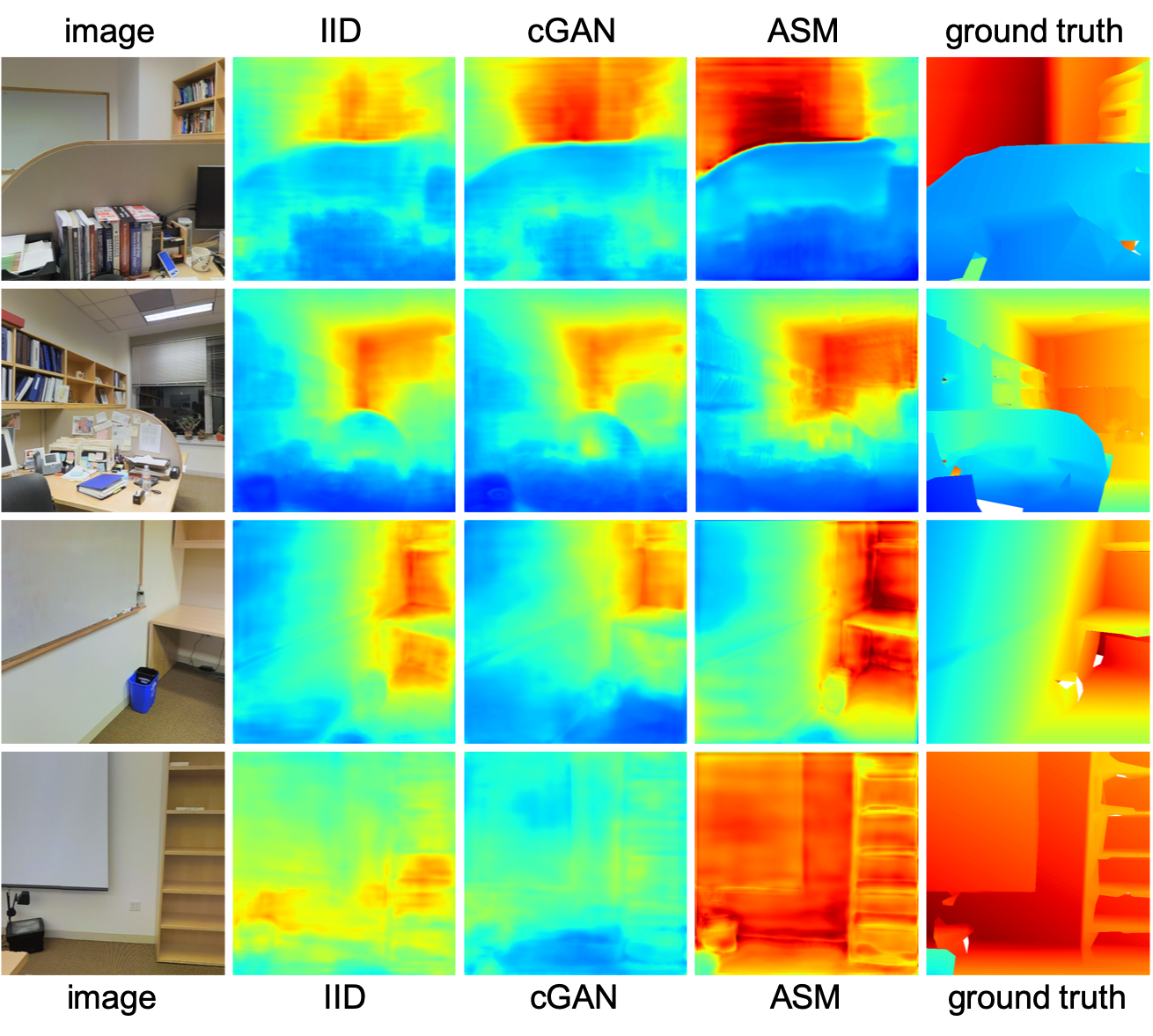
Monocular Depth Estimation on Stanford-2D-3D-Semantic